| Version 97 (modified by dgoll, 8 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
ORCHIDEE-CN-P (former branch ORCHIDEE-CNP)
This page describes the phosphorus cycle in ORCHIDEE-CN-P. It is based on ORCHIDEE-CN, which was extended and corrected as described here: https://forge.ipsl.jussieu.fr/orchidee/wiki/Branches/MergeOCN/Goll as well as additional non-documented bugfixes to avoid negative pools due to machine precisions as well as bugs.
The phosphorus cycle is an adaptation of the the model described by http://www.biogeosciences.net/9/3547/2012/bg-9-3547-2012.html . Nonetheless, the complexity was substantially increased due to the more detailed representation of the C and N cycle in ORCHIDEE compared to JSBACH.
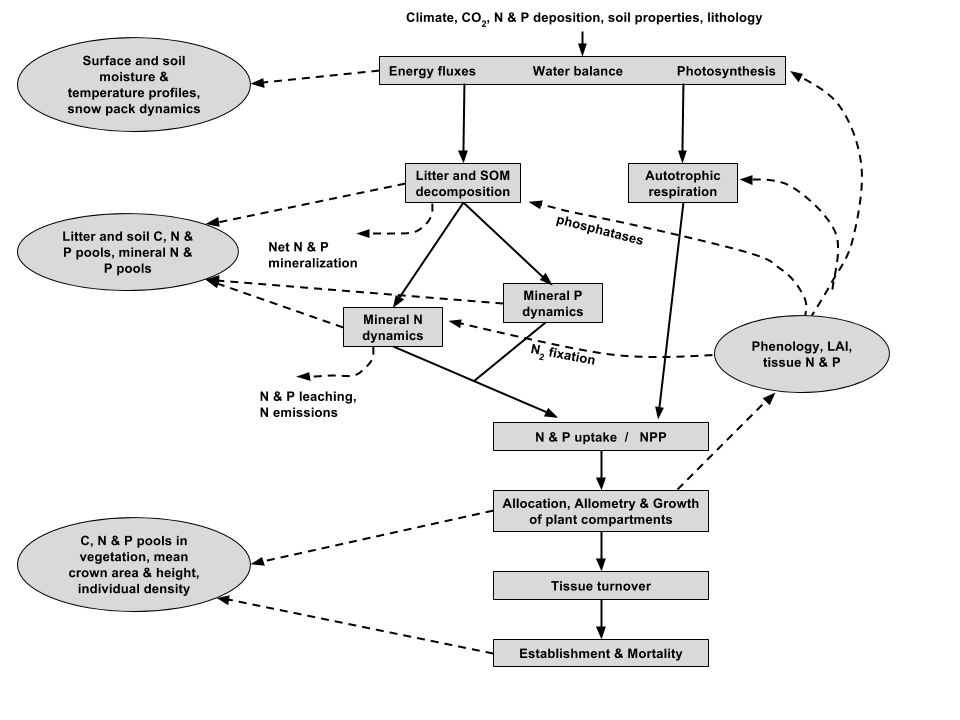 Schematic representation of the key processes represented in ORCHIDEE-CNP
Schematic representation of the key processes represented in ORCHIDEE-CNP
1. Technical notes A: the modularisation of code used by nitrogen and phosphorus routines
There are aspects which the nutrient cycles have in common, for example root uptake kinetics, stoichiometric considerations, etc. To avoid the risks of introducing inconsistencies and reduce redundant code, I introduced the following subroutines. All subroutines are in stomate_phosphorus.f90.
1.1 root_conductivity
This subroutine calculates the uptake capacity of N & P per mass root according to the uptake kinetics of ammonia and nitrate used in OCN (Zaehle & Friend, 2010).
1.2 f_XY_plant
This subroutine calculates the scaling functions based on the stoichiometric ratio of labile plant tissue (reserve, labile and leaf) which are used to scale root uptake, biological N2 fixation, and biochemical mineralization. It currently supports scaling functions based on the P-to-N ratio, N-to-C ratio and P-to-C ratio. All other combinations will cause a 'STOP', but could be easily implemented if needed.
2. Technical notes B: the analytical spinup of the biogeochemical cycles
FAILS 2.1A avoid that immobilisation demand exceeds mineral nutrient supply
Directly, after an analytic spinup cycle the immobilisation demand can exceed the mineral nutrient supply (soil_n_min or soil_p_min). In such a case, we have to add artificially the needed amount of nutrients to the supply. The flag ok_spunup controls that only in the timestep after the analytical solution is derived nutrients can be added.
WORKS 2.1B avoid that immobilisation demand exceeds mineral nutrient supply
During the an analytic spinup cycle the immobilisation demand can exceed the mineral nutrient supply (soil_n_min or soil_p_min). In such a case, we have to add artificially the needed amount of nutrients to the supply. Every time it is needed during spinup.
2.2 prescribed N inputs from BNF during the spinup
The biological fixation of N2 from the atmosphere is computed as a function of NPP and plant C:N:P stoichiometry. During the spinup large amounts of organic matter accumulate which is connected with a high immobilisation flux. We thus must ensure that the N inputs are rather high and constant in time. Therefore we read BNF rates in from a file rather than computing them dynamically.
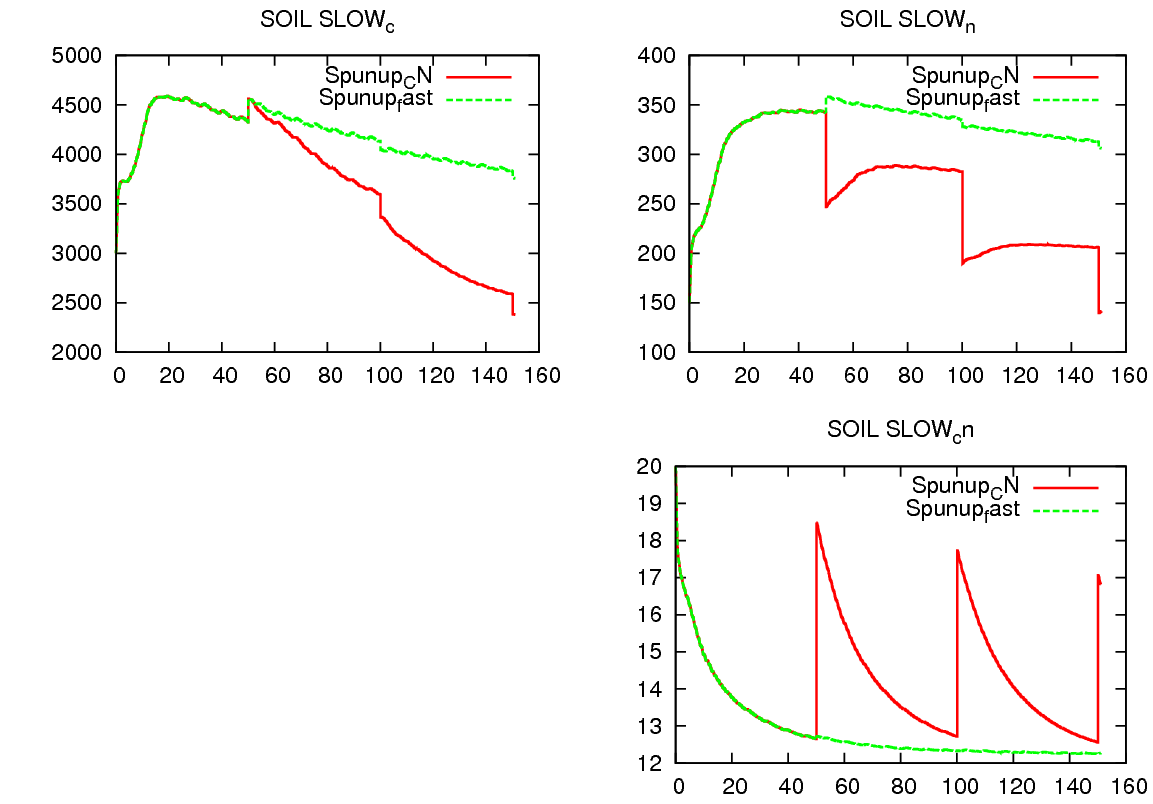
2.3 SOLVED speed up the spin up of soil CNP stoichiometry
It was more like a bugfix. The running window of the average of CN_som_litter_longterm should be limited to a given period not to "unlimited" for the case you want to run long spin up cycles (spinup_period=50yr).
TODO: It would be good to have an automatized test if the mineral N & P cycles are in equilibrium comparable like it is done with the C pools.
3. Conceptual modifications to the nitrogen cycle
3.1 soil mineral N concentration in soil solution
Following Smith et al (2014), I introduced the use of the maximum water holding capacity of soils (max_var_eau) to approximate pore space which to derive the average soil mineral N concentration in solution. The use of the actual water volume can not be recommended as we this would lead to high N concentration in soil water when soil water is very low. As we do not account for the inhibition of replenishment of mineral N in the soil solution around roots when soil water is scarce.
3.2 Biological N2 fixation (BNF)
We introduce a module which computes BNF as a function of NPP, tissue C:N, and tissue & N:P. This approach is based on Cleveland et al (1999), Thornton et al. (2007), and Goll et al. (2012). When using the analytical spinup the BNF must be read in from a file to speed up the spin up. The file should contain the reference BNF rates for the respective climatic conditions. Such files are currently missing, but should be generated as soon as the model is ready.
3.3 Respiration from labile carbon
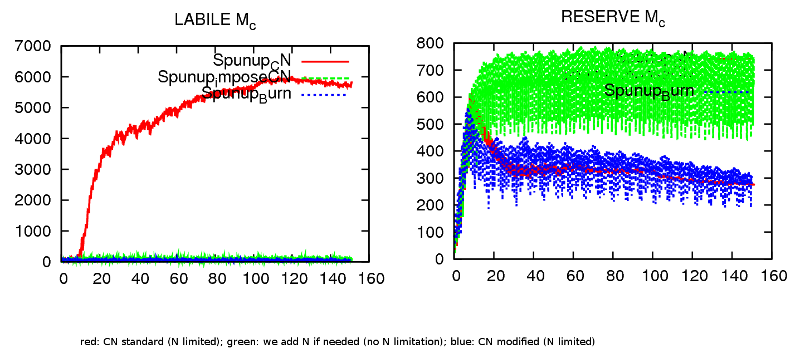
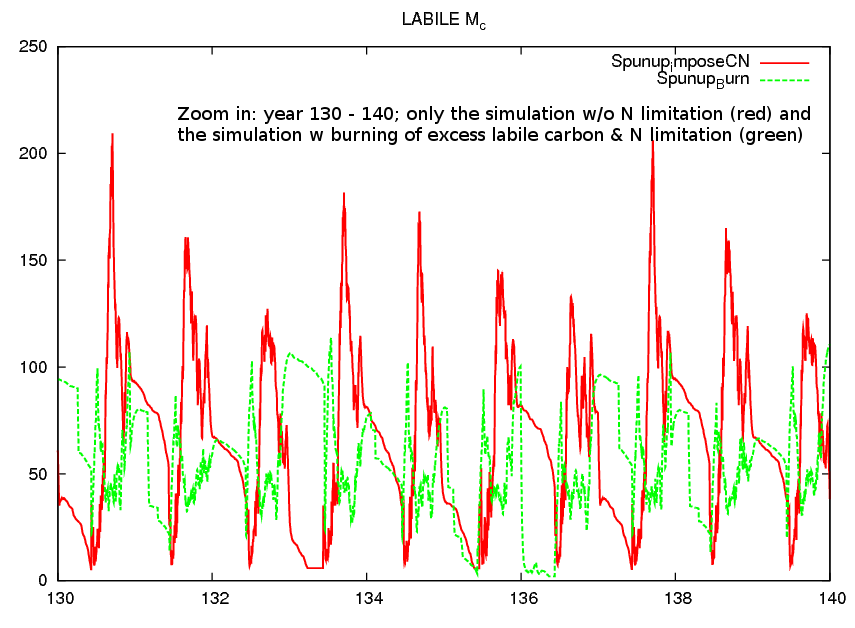
The original formulation of the burning of excess labile carbon was removed by DOFOCO team, to ensure forest grow back after coppicing. This means that labile carbon can accumulated in plants forever without any restrictions as there is no respiration costs associated with this carbon. Thus, nutrient limitation on allocation will lead to accumulation of labile carbon as long as plants can sustain some leaves.
To fix this: I re-introduced the burning of excess labile carbon following Zaehle & Post (2010). It helps to avoid the accumulation of labile carbon; but more tests are needed, in particular FLUXNET site scale evalution is needed.
3.4 SOM stoichiometry
I disabled the flexibility in SOM stoichiometry for the start. We can activate later when everything else is calibrated.
4. New input files
You can find information on the new input files needed for the P cycle here: https://forge.ipsl.jussieu.fr/orchidee/wiki/DevelopmentActivities/ORCHIDEE-CNP/newInput
5. unresolved Issues
There are still unresolved issue with the model. They are listed here: https://forge.ipsl.jussieu.fr/orchidee/wiki/DevelopmentActivities/ORCHIDEE-CNP/issues
6.0 Howto install, compile & run the model
You can find information on how to setup the simulations here: https://forge.ipsl.jussieu.fr/orchidee/wiki/DevelopmentActivities/ORCHIDEE-CNP/howtoUse
Attachments (11)
- missingPoints.png (20.5 KB) - added by dgoll 8 years ago.
-
USDA_map.png
(82.4 KB) -
added by dgoll 8 years ago.
The input file with the USDA soil orders in alphabetical order
-
USDA_map.2.png
(76.8 KB) -
added by dgoll 8 years ago.
input file with USDA soil orders in alphabetical order
-
USDA_map.3.png
(76.0 KB) -
added by dgoll 8 years ago.
The input file with the USDA soil orders in alphabetical order
-
lith_dom_map.png
(96.2 KB) -
added by dgoll 8 years ago.
dominant lithology
-
soilshield_map.png
(83.9 KB) -
added by dgoll 8 years ago.
soil shielding factor
-
ORC-CNP.png
(69.6 KB) -
added by dgoll 8 years ago.
Schematic representation of the key processes represented in ORCHIDEE-CNP
-
CNP_longterm.png
(46.6 KB) -
added by dgoll 8 years ago.
In red original formulation, in green the 3yr average. Shown is the C, the N and the CN of slow soil pool.
- BurnLabile.png (106.3 KB) - added by dgoll 8 years ago.
- Zoom.png (57.2 KB) - added by dgoll 8 years ago.
-
GPP_Hai.png
(48.2 KB) -
added by dgoll 8 years ago.
average annual cycle of DE-Hai site w & w/o N-limitation / w & w/o burning
Download all attachments as: .zip